Chapter 23 Side note to the fourth quarter
If it is one of the "Nine Numbers" in the pre-Qin Dynasty, Zhang Cang and Geng Shouchang in the Western Han Dynasty changed their name to Pythagorean after they learned about the Pythagorean shape and other content, and became the "Nine Chapters" Pythagorean Chapter.According to Jia Xian and Yang Hui's reminder, the above-mentioned Pythagorean Rongfang, Rongyuan and the eight prediction questions are secondary content.We now introduce this type of prospecting problem.There is a square city, I do not know its size, and the gates are all in the middle of the city wall.There is a tree 20 steps out of the north gate.14 steps out of the south gate and 1775 steps to the west, you can see this tree.How long is each side of the city?Let the side length of the city be x, exit the north gate a, exit the south gate k, turn west b, as shown in Figure 21(1), consider two similar Pythagorean, the small Pythagorean b=1/2x, the large Pythagorean Shape hook a=a+x+k.Since a/b=a/b, or a/1/2x=(a+x+k)/b, x+(a+k)x=2ab.This is Liu Hui's first method of deriving this formula.The second method is: as shown in Figure 21(2), the width is DF=x, and the length is BC=x+a+k. The rectangle DEGF has an area x(x+a+k), and then considers the width BC=x+ a+k, the rectangle BCAI whose length is AC=b, is bisected by the diagonal. Since the Pythagorean AAJ is equal to AAG, the areas of BCJI and BCGF are equal. The area of DEGF is twice that of BCGF, that is, twice that of BCJI. The area of BCJI is ab, so x(x+a+k)=2ab.
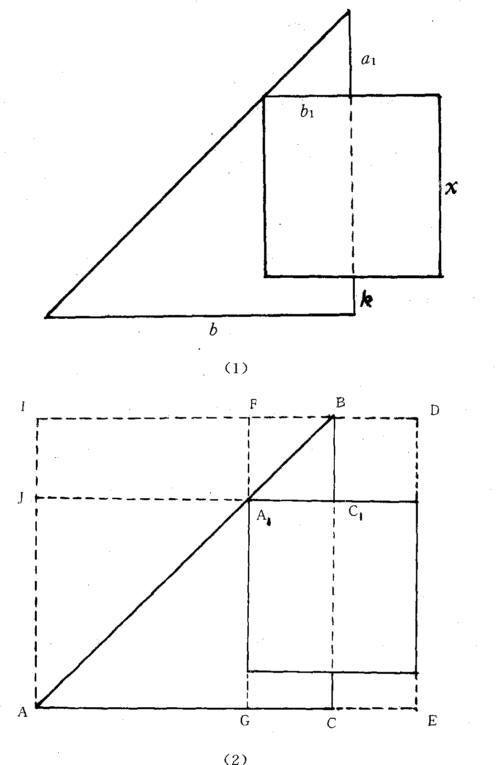
Figure 21 North and South Gates of Chueup
The key of the second method is that the areas of rectangle BCJI and BCGF are equal, and they have a common part BCAF, then the area of rectangle FAJI and CCGA are equal.This is an important principle, which was later summarized by Jia Xian and Yang Hui as follows: if a rectangle is obliquely decomposed into two Pythagorean shapes, the areas of the two rectangles described by the two Pythagorean shapes with any point on the common chord as the common point are equal, see Figure 22.This principle is particularly useful in the complementation of in and out in the problem of prediction. "Nine Chapters" set up four tables to look far away, look at mountains because of trees, and log diameter problems, all of which can be solved in this way.For example, if you look at the mountain from Yinmu and ask: There is a tree 9 feet 5 feet high, 53 miles away from the mountain, and the height of a human eye is 7 feet.Looking at the mountain 3 miles away from the tree, people's eyes, the top of the tree, and the top of the mountain form a straight line.How high is the mountain?Figure 23.According to the above principle, the shaded parts are equal, so ab=ab, so a=ab/b.
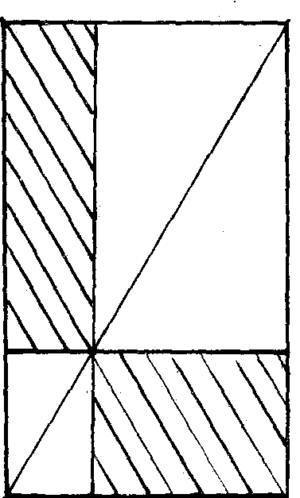
Figure 22 The principle of capacity horizontal capacity straight
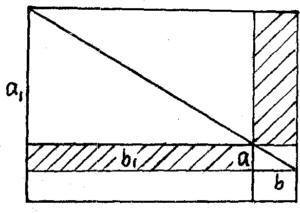
Figure 23 Looking at the Mountain in Yinmu

Figure 21 North and South Gates of Chueup

Figure 22 The principle of capacity horizontal capacity straight

Figure 23 Looking at the Mountain in Yinmu
