Chapter 14 Section 2 The Essence of Painted Pottery
Painted pottery is a concentrated expression of the aesthetic taste of prehistoric ancestors and a concentrated expression of prehistoric artistic achievements.
Since the invention of pottery, its decoration has been valued by prehistoric craftsmen, and all means have been mobilized as much as possible, including the use of grinding, carving, embossing methods, especially the application of colored painting, which makes the rough texture of pottery colorful. .People from Baijia Village were the first to paint and decorate pottery. Later, Yangshao people greatly developed the art of painted pottery, and Majiayao people pushed the development of this art to its peak.Painted pottery is a concentrated expression of human wisdom and creativity, and is also an important content of prehistoric culture. Some researchers often call it "painted pottery culture".
Prehistoric painted pottery in China has a wide distribution and a long time span.The art of painted pottery began 8,000 years ago and lasted until the end of the Neolithic Age, about 4,000 years ago.The prosperous period of painted pottery was roughly 6,500-4,500 years ago, or more than 2,000 years ago.In such a span of time, most Neolithic culture residents made painted pottery, but there were great differences in quantity and style.The Yangshao, Dawenkou, Daxi, Qujialing, and Majiayao cultures with relatively developed painted pottery crafts are concentrated in the Yellow River Basin and the middle reaches of the Yangtze River, with the central area in the middle and upper reaches of the Yellow River.Painted pottery has also been found in South China and North China, but the quantity is very small, far from being comparable to that in the Yellow River Basin.
Prehistoric painted pottery has a variety of patterns and motifs.The decorations often depicted by different cultural communities are different. It can be seen that the themes they express are different, and the selection of colors also has their own characteristics, forming their own traditional characteristics.
The painted pottery of the early Yangshao Culture is dominated by red ground and black colors, and the decorations are mostly animal shapes and their variants, with a strong realistic style. The motifs include fish, fishnets, deer, birds, frogs, human faces, etc., as well as broken lines and triangles. Geometric decorations such as dots and dots are mostly expressed in straight lines.In the later period, in addition to the black color on the red ground, white clothes and black color appeared again, and there were also realistic motifs such as birds, fish, and frogs. Figure 9).
Majiayao culture painted pottery has a large number of rich and vivid colors, and several colors of red, black and white are used together.The patterns are also very rich, and there are more complex pattern combinations. The common motifs include swirls, concentric circles, waves, parallel lines, grid patterns, broken lines, toothed belt patterns, etc. The lines are smooth and changeable, with a strong sense of movement. (Figure 10).
Painted pottery of the Daxi culture also has its own characteristics. Black pottery is painted on red pottery, and red pottery is painted on black pottery.Qujialing culture has unique Zhuhui black pottery, eggshell painted pottery, and painted spinning wheel. The colors are orange yellow, orange red and black, and a kind of smudge painting method is used, which is different from the common hook line coloring. The method of decoration mainly includes geometric shapes such as swirls and arcs, and most of the compositions are relatively simple.
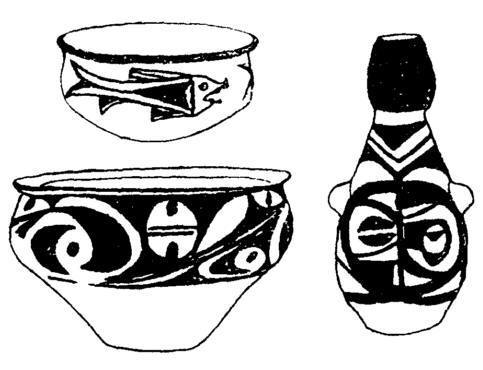
Figure 9 Painted pottery of the Yangshao Culture
There is also a certain amount of painted pottery in Dawenkou Culture, with black, white, red, and ochre, and decorated with grid patterns, petal patterns, octagonal star patterns, broken lines, and swirl patterns, almost all of which are geometric shapes.
Some painted pottery decorations are only seen in a certain culture, and some decorations will arouse the consensus of residents of a certain cultural tradition and be loved by them. From this, we can see the fact of cultural exchanges and also show a certain sense of cultural integration. .For example, the common flower petal patterns in Yangshao Culture painted pottery are found in Dawenkou, Daxi and other cultures. The distribution covers almost the entire Yellow River Basin and the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, and the ages are also very close. The composition shows that Surprisingly similar.This seems to indicate that the petal pattern has a certain meaning, which is easily accepted by residents of different traditions.
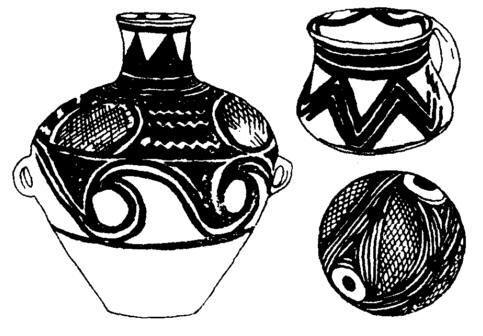
Figure 10 Painted pottery from the Majiayao Culture
On the whole, painted pottery decorations usually adopt a variety of geometric patterns, and human-shaped and animal-shaped compositions are rarely seen.Many researchers believe that many geometric patterns are the result of the deformation and simplification of animal patterns, and their essence is still some animals, so they should still be treated as animal patterns. This statement has some truth.Some triangular painted pottery decorations found in Banpo are obviously evolved from fish patterns (Fig. 11).
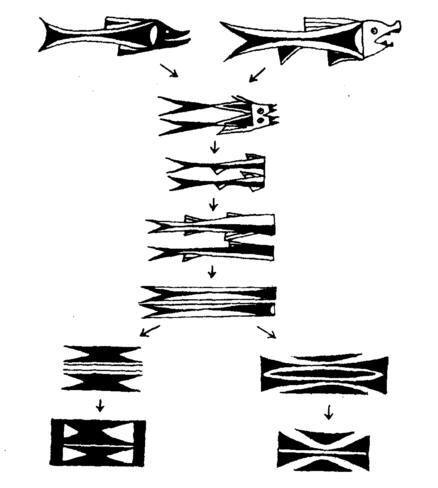
Figure 11 The evolution from fish patterns to geometric patterns on painted pottery of the Yangshao Culture
As far as the painted pottery unearthed in the Qinghai area of Gansu Province is concerned, the ancestors of many geometric pattern motifs are elephantine motifs, and the evolution track of some is quite clear.For example, straight triangles are formed from the shape of fish body, fish tail or fish fins, swirls are formed from bird head shapes, and zigzagging patterns are simplified from frog patterns and frog limb patterns, so triangles, swirls , wavy lines are recognized as the logo graphics of fish, bird and frog respectively.Judging from this discovery, many geometric figures are indeed transformed from pictorial patterns and have the same symbolic meaning.
Although there are quite a variety of painted pottery decorations, they were not drawn by prehistoric potters at will. There were originally certain rules for what to depict, because common decorations have certain meanings and are restricted by the original cultural tradition.
Pottery painted with colored patterns can not only bring people beautiful enjoyment, but also a kind of image sustenance for the spiritual life of prehistoric residents.People paint painted pottery not only to beautify their lives, but also to express their specific psychology and consciousness, and even express their worldview and so on.Therefore, there are established rules for the choice of ornamentation and composition, and a deep-rooted tradition has been formed in this way.For example, the common frog patterns, bird patterns and their variants in the Yangshao and Majiayao cultures may reflect the psychology of worshiping frogs and birds at that time.In the early days of Chinese civilization, frogs and birds were also worshiped very much. Birds are the god of the sun, and frogs (toads) are the god of the moon. It can be seen that the worship of the sun and the moon is rooted in primitive society. fully displayed in front of us.We have also observed from this that the worship of the sun and the moon in ancient China should have originated in the middle and upper reaches of the Yellow River, and it was a product of primitive farming culture (Figure 12).
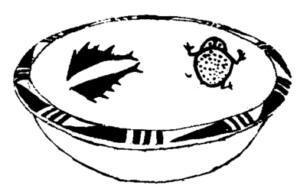
Figure 12 Painted pottery of Yangshao Culture with toad figures
In addition, there are also many painted pottery decorations with mysterious meanings that cannot be understood at a glance.For example, the human-mask-fish pattern painted by Yangshao people can be found in Guanzhong and southern Shaanxi. The basic composition is relatively consistent, but there are different explanations for it. There are as many as 20 kinds, and none of the commentators can convince anyone.It is likely that there are more reasonable arguments already included, but it is not an easy task to test which one is correct (Fig. 13).
The most exquisite masterpiece of painted pottery was discovered in Yancun, Ruzhou, Henan in 1978, and the era belongs to the Yangshao period.On one side of a large flat-bottomed pot with a deep belly, there is a large colored painting: a standing white stork with a large fish in its beak, and a stone ax painted opposite it.This painting is named "Stork Fish Stone Ax Picture", which is different from the general pattern decoration, expressing a certain complete meaning, or at least expressing some kind of desire of people. Such a statement is probably still a mystery to be solved.
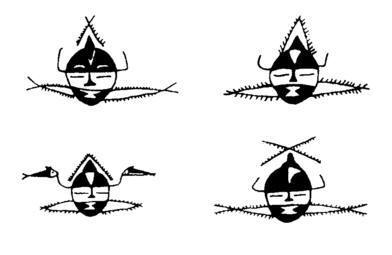
Figure 13 Painted pottery patterns with human faces in Yangshao Culture
Judging from the smooth lines and rigorous composition of painted pottery patterns, brushes for painting have been invented in prehistoric times, although no real brushes have been unearthed at that time.The bright colors come from different mineral pigments, such as hematite powder, kaolin, etc. Ingots of purple and red colors were unearthed from the Beishouling site in Baoji, which are analyzed to be the raw materials for the colors of painted pottery.Stone plates for color research and pottery plates for color mixing have also been found in many ruins. The painting process should be in the hands of some professionals.In a Yangshao culture tomb in Jiangzhai, Lintong, stone inkstones, grinding rods, water cups and hematite blocks were buried on the feet of the deceased, indicating that the owner of the tomb may be a painted pottery craftsman.
Although it is difficult for us to fully understand the artistic conception conveyed by prehistoric artisans through painted pottery patterns, the precious spiritual wealth they created is indeed valuable and rare.

Figure 9 Painted pottery of the Yangshao Culture

Figure 10 Painted pottery from the Majiayao Culture

Figure 11 The evolution from fish patterns to geometric patterns on painted pottery of the Yangshao Culture

Figure 12 Painted pottery of Yangshao Culture with toad figures

Figure 13 Painted pottery patterns with human faces in Yangshao Culture
