Chapter 7 Chapter 2 The City Tells You
State secrets, Beijing knows.
As the capital of the Chinese Empire, Beijing during the Ming and Qing dynasties was extraordinary.Beside the canal-like wide moat, reeds stand tall, willows line the banks, and the shadows of trees dance.Whenever ducks glide across the river, or a breeze brushes through the leaves, the walls reflected in the water begin to vibrate and shatter.Looking up, the city towers and city walls towered abruptly, showing black silhouettes against the clear sky.The wing-like eaves of the gate tower show off the sky, spreading its wings in the air, which is magnificent.Pedestrians rode sleepily on donkeys and entered the city gate. Behind them, the fresh vegetables on the shoulders of the farmers were dripping green, and the unhurried sound of camel bells sounded in their ears.
This is the Beijing described by the Swedish scholar Oswold Xirenlong.To be precise, it was Peking in 1924.It is typical and representative of all imperial capitals in China.Perhaps, the royal city two or three thousand years ago looked like this:
Yes.At the time of Xia Qi, Shang Tang, and Zhou Wu, there should have been no camels.
However, there must be a city.
In fact, all ancient civilizations began with the construction of cities.All ancient civilizations also have their own cities, but some are famous, such as Assyria, Babylon, Memphis, and Jerusalem; Mohenjodaro and Harappa, Nosas and Faeste of Crete.Without cities, it would not be possible.
The history of the founding of the ancient nation is also the history of their city.
Indeed, no matter how large the population of an ethnic group is, no matter how extensive its territory, if it does not have cities, it is only a tribe or tribal alliance, not a country.It is ridiculous for a village head and an accountant to claim the title of president and finance minister.
In fact, even rich landowners have soil enclosures.Expressed as a Chinese character, it is the "or" of or.Or, it is the "country" of the country, which is the earliest national character; it is also the "domain" of the region, which is the earliest domain character.Country, domain, or are the same word in Oracle.The font is a "口" on the left and a "Ge" on the right.口, pronounced like Wai, also means "encircle", that is, circle, wall, sphere of influence.Ge is a servant, thug, bodyguard, and guard.That is to say, once a clan or tribe settles down and has its own territory, it will build a fence or wall, dig a ditch, and send troops to guard it.This is "or".
The territory is getting bigger and bigger, the population is getting bigger and bigger, and the specifications are getting higher and higher.Therefore, if you add soil next to it, it becomes a "domain"; or if you add a mouth, it becomes a "country".Some scholars think that this is superfluous, but it is not necessarily true.After all, the country is not a country, so how can it still be "or"?

The "country" (Mao Gong Ding) in bronze inscriptions.

"Or" in oracle bone inscriptions (Ye Sanxia · Four Three · Four).
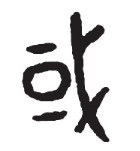
"Or" (Xijiapan) in bronze inscriptions.
(Obviously, country is or.)
How, then, do nations differ from tribes?
city.
There are two ancient civilizations in the world.One is a city plus surrounding rural areas as one country, which is called a "city-state", or "city-state" for short; the other is a central city (capital) plus other cities and their rural areas, which is called a "territorial state".The city-states first appeared in the south of Mesopotamia; the first dynasty of Egypt was a territorial state with Thinis as its capital.
Whether it is a territorial state or a city state, there must be cities, and they must all be centered on cities.
Therefore, country must be "or" plus "口".Or, it only means that there is a territory; 口 means that there is a city.In fact, in ancient Chinese literature, a country is a city, and a city is an entrance. For example, the gate of a country is the gate of the city, and the middle of the country is the middle of the city.If it is a territorial state, the state is the capital.For example, the original meaning of "China" is "in the world", which is the central city of the world.Later, it generally refers to the Central Plains area where Kyoto is located.
As for the so-called "country" today, the ancients called it "state".The word country was originally "state family".Later, because of avoiding the taboo of Han Gaozu, the state was changed into a state.In fact, the country is only the capital city, and the state is the whole territory.Within the city wall is called a country, and within the four borders is called a state.The Federation cannot be called the "United States", the Confederacy cannot be called the "League of Nations", the diplomatic relations cannot be called the "Guojiao", and China cannot be called the "China State".
The secret of the country lies in the city.
Knowing why there are cities, you know why there are countries.
Notes:

The "country" (Mao Gong Ding) in bronze inscriptions.

"Or" in oracle bone inscriptions (Ye Sanxia · Four Three · Four).
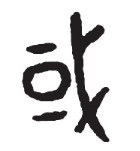
"Or" (Xijiapan) in bronze inscriptions.
(Obviously, country is or.)
Notes:
